-
Products
-
Lab Instruments
Other Instruments
-
Lab Meters and Probes
Calibration Standards Radiometer ProbesOther Reagents
- Chemistries, Reagents, and Standards
-
Online Analysers
Ammonium Analysers Ammonia Monochloramine Chlorine Analysers
- CL17sc
- CL10sc Amperometric
- 9184 sc Amperometric
- Ultra Low Range CL17sc Colorimetric Chlorine Analyser
EZ Series Analysers- Iron
- Aluminium
- Manganese
- Phosphate
- Chloride
- Cyanide
- Fluoride
- Sulphate
- Sulphide
- Arsenic
- Chromium
- Copper
- Nickel
- Zinc
- Ammonium
- Total Nitrogen
- Total Phosphorus
- Phenol
- Volatile Fatty Acids
- Alkalinity
- ATP
- Hardness
- Toxicity
- Sample Preconditioning
- Boron
- Colour
- Nitrate
- Nitrite
- Silica
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- EZ Series Reagents
- EZ Series Accessories
- EZ sc Series Inorganics
- EZ sc Series Metals
- EZ sc Series Nutrients
-
Online Sensors and Controllers
Digital Controllers (Transmitters) Controllers (Analogue)
- SC4500
- Orbisphere 366x Ex
- Orbisphere 410/510 Carbon Dioxide
- Orbisphere 410/510 Oxygen
- Orbisphere 410/510 Ozone
- Orbisphere 51x Hydrogen
Single, Dual, Multi-parameter Online Panels pH & ORP Sensors- 1200-S ORP
- 1200-S pH
- 12mm pH/ORP
- 8362 sc High Purity
- Combination pH/ORP
- Differential pH
- Digital Differential ORP
- Digital Differential pH
- LCP ORP
- LCP pH
Conductivity Sensors- 3400 Analogue Contacting
- 3400 Digital Contacting
- 3700 Analogue Inductive
- 3700 Digital Inductive
- 3798 sc Electrodeless
- 9523 Cation Conductivity
- 9525 DCCP System
-
Automated Lab Systems
Robot Systems
- Multiparameter Online Panels
- Claros Water Intelligence System
- Samplers
- Test Kits & Strips
-
Lab Equipment and Supply
Apparatus
- Brushes
- Clamps, Rings & Stands
- Crucibles
- Crucibles & Casseroles
- Dispensers & Droppers
- Grab Samplers
- Oil and Grease
- Other Apparatus
- Pipet Aids
- Pipettes
- Racks
- Stir Bars
- Tubing
- Weighing Accessories
General Lab Consumables Glassware/PlasticwareInstruments -
Microbiology
Accessories and Chemicals Dehydrated MediaLabware
- Electrochemistry
-
Lab Instruments
- Parameters
-
Software Solutions
-
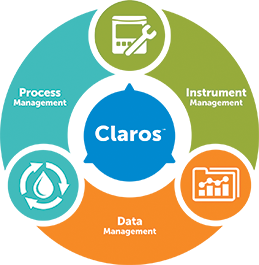
Claros Water Intelligence System
Product Pillars Process Management
- Solutions For:
- BOD/COD Removal
- Nitrification/Denitrification
- Phosphorous Removal
- Sludge Management
Data Management- Solutions For:
- Collection
- Visualization & Analytics
- Reporting
- Data Accuracy
Instrument Management- Solutions For:
- Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Remote Access
- Lab and Process Comparison
Industry Challenges Regulatory Compliance Cost Savings Remote Operations Process Optimisation Equipment Maintenance
-
Claros Water Intelligence System
- Industries
- Service
- News & Events